As of 2024, global progress toward achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 2030 has been mixed. India is also in the quest of achieving them timely, but its progress is intricately linked to addressing regional disparities across its states and union territories. The NITI Aayog’s SDG India Index 2023-24 reveals significant variations in progress, underscoring the challenges these disparities pose to the nation’s overall advancement.
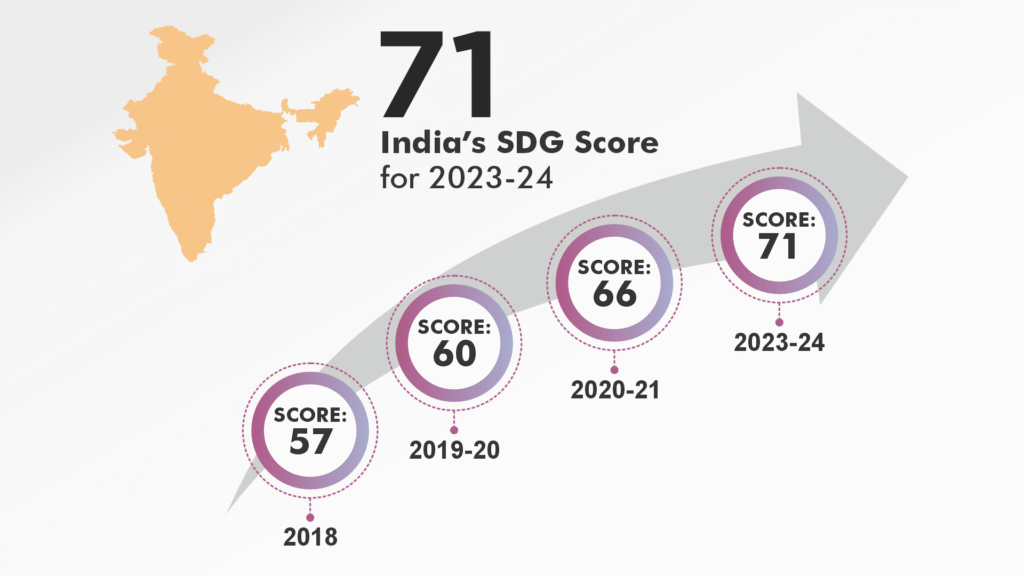
As per SDG India Index 2023-24, India’s national SDG score improved to 71 in 2023-24, up from 66 in 2020-21. This reflects advancements in areas like poverty eradication, economic growth, climate action, and life on land. However, this national progress conceals substantial inter-state disparities. States like Sikkim and Goa have achieved higher per capita incomes, with Sikkim’s per capita income estimated at approximately ₹588,000 in the FY 2024, and Goa’s at around ₹492,648. In contrast, Bihar’s per capita income remains significantly lower, estimated at over ₹60,000 during the same period.
These economic disparities are further accentuated at the district level. For example, in Uttar Pradesh, the per capita Net State Domestic Product (NSDP) was reported at ₹93,514 in March 2024, reflecting an increase from ₹84,125 in March 2023. Such disparities highlight the uneven distribution of economic development within states.
These pronounced disparities pose significant challenges to India’s attainment of the SDGs. States lagging in economic development, infrastructure, healthcare, and education may struggle to meet targets related to poverty alleviation, quality education, and health and well-being. The uneven distribution of resources and opportunities can hinder national efforts to achieve inclusive and sustainable development.
To mitigate these challenges, a multi-faceted approach is essential. Implementing policies tailored to the specific needs of underperforming regions can address unique challenges and leverage local strengths. Enhancing education and skill development programs can improve productivity and economic prospects.
Besides this, improving physical and digital infrastructure can attract investments and facilitate economic activities. Strengthening institutional capacities at the local level can ensure the effective implementation of development programs. Addressing regional disparities is crucial to fostering equitable growth and development across all regions of the country. It will help the nation to ensure steady progress toward sustainability so that no one can be left behind.