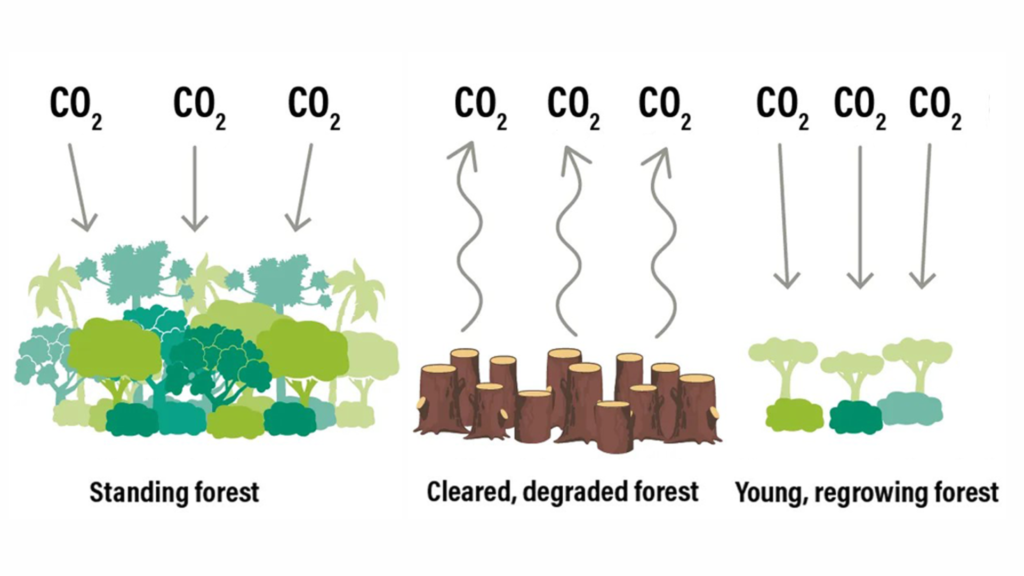
The shrinking of global carbon sinks, especially forests, due to climate change and human activities like deforestation presents a growing threat to environmental sustainability. Forests, which historically absorbed significant amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), are now struggling to maintain this function due to rising degradation, particularly in tropical regions. The ability of forests to sequester carbon is being undermined by factors such as deforestation, land-use changes, and climate-driven phenomena like increased wildfires and droughts.
According to the World Resources Institute (WRI), forests currently absorb roughly 15.6 gigatons of CO2 each year—double what they emit. Thus, forests become an indispensable element in mitigating climate change scenarios. However, human activities, including agriculture and logging, have drastically reduced this carbon-absorbing capacity. The Amazon forests which are known as the “lungs of the Earth” have been continuously turning into a carbon source from a carbon sink because of rising incidents of deforestation and fires.
Dried forests are a pressing concern as global warming is leading to more frequent droughts and rising temperatures, which in turn dry out forests, particularly in tropical regions. This obstructs their ability to photosynthesize and restricts their ability to absorb CO2. The scientific community is critically analyzing its impact on the environment and biodiversity conservation.
The long-term impact of losing these critical carbon sinks extends beyond climate. Forests play a crucial role in preserving biodiversity, controlling water cycles, and ensuring local climate stability. The degradation of forests disrupts these functions, leading to hotter and drier conditions, more frequent wildfires, and the collapse of biodiversity. This triggers a vicious cycle of further forest loss, creating far-reaching, cascading effects across ecosystems and human communities alike, making the challenge even harder to reverse.Top of FormBottom of Form
To address this, global initiatives such as afforestation, reforestation, and the enforcement of stricter deforestation laws are critical. Countries are focusing on aligning their initiatives to preserve forests on priority. Thorough carbon reduction strategies to decrease emissions and limit global temperature rise to 1.5°C, under the Paris Agreement have been placed. Additionally, integrating local communities and indigenous knowledge into forest conservation practices further strengthens these initiatives to bring realistic changes.